18F-FC303
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is the second most common cancer in worldwide, and the 5th leading cause of deaths among men in Korea. Prostate cancer incidence rate tends to rapidly increase due to “Western” diet/life style and the growth of elderly population. While the incidence rates for stomach-, liver-, and lung cancers have been declining, prostate cancer incidence rate is annually increased by more than 10%. The early stage-prostate cancer has small size and no symptom or signs. However, according to prostate cancer progression, several urological symptoms occur including urinary and bladder problems. The progression of prostate cancer usually slow, but when it advanced to malignancy or invasive metastasis, it’s treatment is extremely difficult. The metastasis usually begins around the primary tumor such as lymph nodes, pelvic bones, spine and bladder, gradually spreading to whole body. In particular metastases occurring in the pelvic bones or spine can lead to severe bone pain, ultimately can lead to paraplegia.
Current diagnosis/treatment, and problems
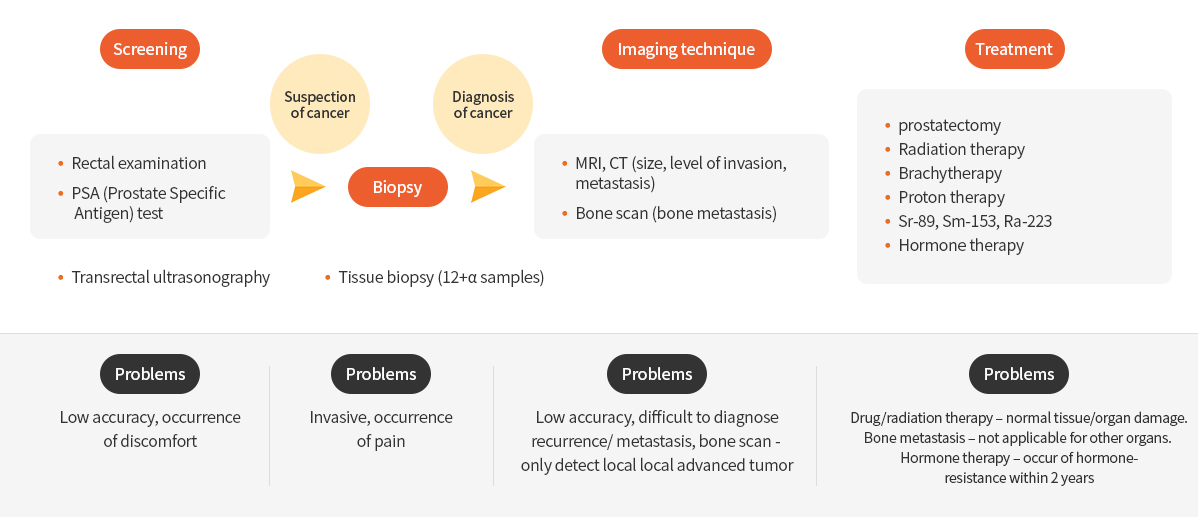
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
When prostate cancer is suspected due to urinary problems, several tests such as rectal examination, blood PSA test, transrectal ultrasonography are performed for diagnosis. Tissue biopsy is performed for prostate cancer confirmation. Medical imaging including CT, MRI, and WBBS (Whole body Scan) is used for prostate cancer diagnosis. However, these diagnostic methods not only cause pain and discomfort, but are also indistinguishable from benign diseases such as inflammatory diseases and prostatic hyperplasia. Therefore, non-invasive PET imaging is required for accurate prostate cancer diagnosis. 18F-FDG is the most commonly used radiopharmaceutical for the diagnosis of various cancers. However, 18F-FDG is not used for the prostate cancer diagnosis due to its low uptake.
PSMA
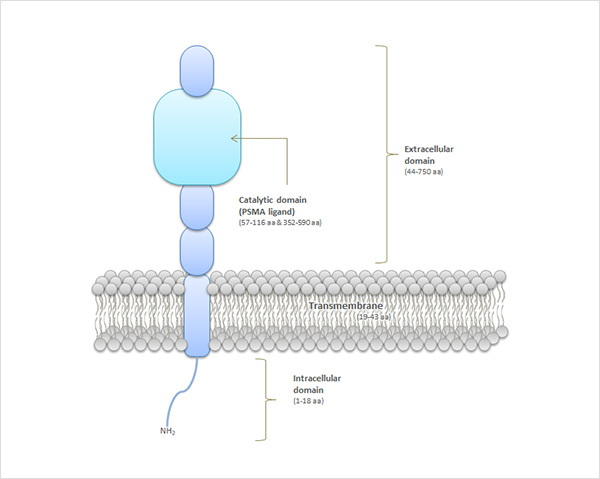
Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen (PSMA) is a membrane protein that is composed with 750 amino acids (Figure 1). PSMA overexpressed in prostate cancer cells. So, PSMA has become a useful biomarker for prostate cancer diagnosis. The extracellular portion of PSMA has an enzymatic ability to hydrolyze the substrate. For this reason, PSMA target glutamate-urea-lysine based compounds that has similar the chemical structure with substrates, are being developed worldwide.
18F-FC303
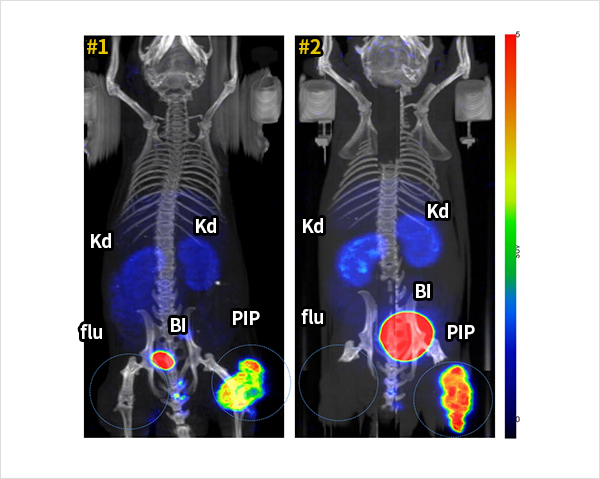
18F-FC303 is a 18F-labeled PSMA- specific targeted compounds that selectively accumulates in prostate cancer. In vivo microPET/CT imaging using prostate cancer mouse model, 18F-FC303 showed clear tumor lesion imaging due to its high tumor to non target tissue uptake ratio compared to 18F-DCFPyl (PET drug candidate developed in the US). Figure 2 is a MicroPET/CT image acquired at 90 minutes after the injection of 18F-FC303 into tumor-grafted mouse. PSMA positive PC3-PIP prostate cancer cell line and PSMA negative PC3-flu cell line was xenografted to right and left thighs of mouse, respectively. The images show high uptake of 18F-FC303 in PC3-PIP cancer in two mice while extremely low uptake in normal organs except bladder. Since 2017, production and quality control of radiopharmaceuticals for clinical trials must meet international guidance on Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) as same as nonradioactive radiopharmaceuticals in Korea. For this reason, we developed own technology for sCUBE® automation module, for a automated synthesis and production of high-dose of 18F-FC303 . Automated synthetic systems with modules are indispensable for the development of 18F-labeled radiopharmaceuticals. Fluorine-18 has short half-life (110 minutes), thus 18F-labeled radiopharmaceuticals must be produced shortly before the use for diagnosis. A uniform quality of 18F-FC303 production was enabled by certain process of sCUBE® module. 18F-FC303, produced by sCUBE® module, meets all standards for 10 quality control items.
Preclinical studies of 18F-FC303
Single-dose toxicity test was performed in rats and beagle dogs, and showed no mortality or adverse effect up to 1,000 times estimated clinical application dose. Also, there were no abnormalities in safety pharmacology test results. Radiation dosimetry studies confirmed that exposed radiation is 3 times lower than 18F-FDG which is used for diagnosis of cancers.
Clinical studies of 18F-FC303
After obtaining clinical trial plan approval for 18F-FC303, Phase 0 study was conducted at Korea Cancer Center Hospital. Phase 0 study, also called micro-dosing study, is a study used to increase clinical trial success rate by observing pharmacokinetics in human body with very small amount of drug. In case of PET radiopharmaceuticals, this study can be a good tool to determine further development of the drug by measuring diagnostic performance of the drug with PET scan on healthy controls and patients.
